Difference between revisions of "Sulzberger Ice Shelf"
Westarctica (talk | contribs) (Created page with "The '''Sulzberger Ice Shelf''' (77°0′S 148°0′W) is an ice shelf about 137 km (85 mi) long and 80 km (50 mi) wide bordering the coast of Westarctica bet...") |
Westarctica (talk | contribs) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
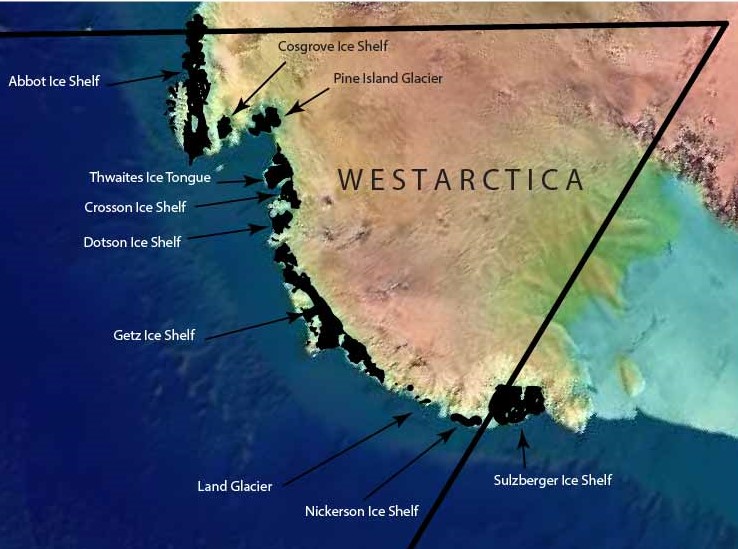
[[File:ice features.jpg|right|600px|Major ice features of Westarctica]] | |||
The '''Sulzberger Ice Shelf''' (77°0′S 148°0′W) is an [[ice-shelf|ice shelf]] about 137 km (85 mi) long and 80 km (50 mi) wide bordering the coast of [[Westarctica]] between [[Edward VII Peninsula]] and the [[Guest Peninsula]]. | The '''Sulzberger Ice Shelf''' (77°0′S 148°0′W) is an [[ice-shelf|ice shelf]] about 137 km (85 mi) long and 80 km (50 mi) wide bordering the coast of [[Westarctica]] between [[Edward VII Peninsula]] and the [[Guest Peninsula]]. | ||
[[Cronenwett Island]], a large island bisected by the 150 degree line of longitude, is claimed in equal halves by Westarctica and New Zealand's [[Ross Dependency]] | |||
==Discovery and name== | ==Discovery and name== | ||
| Line 5: | Line 8: | ||
==Tsunami ice bergs== | ==Tsunami ice bergs== | ||
[[ | The ice shelf released [[iceberg]]s within a day of the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. Scientists have linked the ice calving to the tsunami reaching the [[ice shelf]], some 13,600 kilometers (8,500 mi) away from the earthquake epicenter. The main iceberg was approximately the area of Manhattan Island. In total, the icebergs calved from the ice shelf totaled an area of nearly 125 km2 (48 mi2). This section of the shelf had not moved since 1946. | ||
[[File:Ice shelf bergs.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Satellite images of ice bergs breaking away]] | |||
[[Category:Ice Shelves]] | [[Category:Ice Shelves]] | ||
[[Category:Geography of Westarctica]] | [[Category:Geography of Westarctica]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:15, 17 May 2018
The Sulzberger Ice Shelf (77°0′S 148°0′W) is an ice shelf about 137 km (85 mi) long and 80 km (50 mi) wide bordering the coast of Westarctica between Edward VII Peninsula and the Guest Peninsula.
Cronenwett Island, a large island bisected by the 150 degree line of longitude, is claimed in equal halves by Westarctica and New Zealand's Ross Dependency
Discovery and name
The ice shelf was observed and roughly mapped by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition on 5 December 1929, and named by Richard E. Byrd for Arthur H. Sulzberger, publisher of The New York Times, a supporter of the Byrd expeditions in 1928–1930 and 1933–1935.
Tsunami ice bergs
The ice shelf released icebergs within a day of the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. Scientists have linked the ice calving to the tsunami reaching the ice shelf, some 13,600 kilometers (8,500 mi) away from the earthquake epicenter. The main iceberg was approximately the area of Manhattan Island. In total, the icebergs calved from the ice shelf totaled an area of nearly 125 km2 (48 mi2). This section of the shelf had not moved since 1946.