Difference between revisions of "Template:Westarctica.wiki:Today's featured article"
Westarctica (talk | contribs) |
Westarctica (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Icesheet-Map.jpg|thumb|300px|left]] | ||
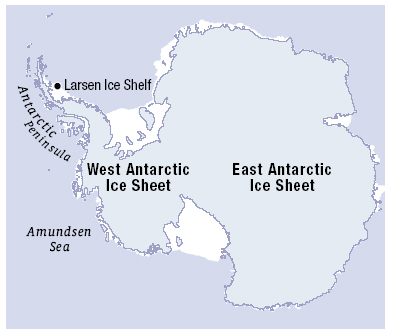
'''[[ | The '''[[West Antarctic Ice Sheet]]''' (WAIS) is the segment of the continental ice sheet that covers [[Westarctica]] and the portion of [[Antarctica]] on the side of the [[Transantarctic Mountains]] which lies in the Western Hemisphere. The WAIS is classified as a marine-based ice sheet, meaning that its bed lies well below sea level and its edges flow into floating [[ice-shelf|ice shelves]]. The WAIS is bounded by the [[Ross Ice Shelf]], the [[Ronne Ice Shelf]], and outlet [[glacier]]s that drain into the [[Amundsen Sea]]. | ||
Under the force of its own weight, the ice sheet deforms and flows. The interior ice flows slowly over rough bedrock. In some circumstances, ice can flow faster in ice streams, separated by slow-flowing ice ridges. The inter-stream ridges are frozen to the bed while the bed beneath the ice streams consists of water-saturated sediments. Many of these sediments were deposited before the ice sheet occupied the region, when much of West Antarctica was covered by the ocean. The rapid ice-stream flow is a non-linear process still not fully understood; streams can start and stop for unclear reasons. | |||
'''([[ | '''([[West Antarctic Ice Sheet|Full Article...]])''' | ||
Revision as of 05:12, 11 February 2019
The West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) is the segment of the continental ice sheet that covers Westarctica and the portion of Antarctica on the side of the Transantarctic Mountains which lies in the Western Hemisphere. The WAIS is classified as a marine-based ice sheet, meaning that its bed lies well below sea level and its edges flow into floating ice shelves. The WAIS is bounded by the Ross Ice Shelf, the Ronne Ice Shelf, and outlet glaciers that drain into the Amundsen Sea.
Under the force of its own weight, the ice sheet deforms and flows. The interior ice flows slowly over rough bedrock. In some circumstances, ice can flow faster in ice streams, separated by slow-flowing ice ridges. The inter-stream ridges are frozen to the bed while the bed beneath the ice streams consists of water-saturated sediments. Many of these sediments were deposited before the ice sheet occupied the region, when much of West Antarctica was covered by the ocean. The rapid ice-stream flow is a non-linear process still not fully understood; streams can start and stop for unclear reasons.