Template:Westarctica.wiki:Today's featured article
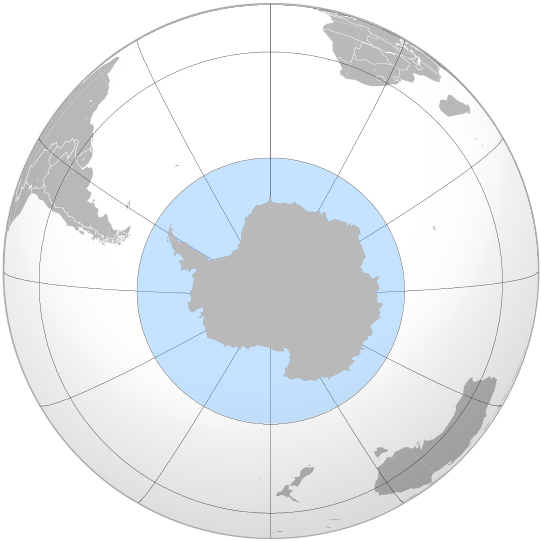
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling the continent of Antarctica. As such, it is regarded as the fourth-largest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. This ocean zone is where cold, northward flowing waters from the Antarctic mix with warmer subantarctic waters. The Southern Ocean, geologically the youngest of the oceans, was formed when Antarctica and South America moved apart, opening the Drake Passage, roughly 30 million years ago. The separation of the continents allowed the formation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current.
According to Commodore John Leech of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), recent oceanographic research has discovered the importance of Southern Circulation, and the term "Southern Ocean" has been used to define the body of water which lies south of the northern limit of that circulation. This remains the current official policy of the IHO, since a 2000 revision of its definitions including the Southern Ocean as the waters south of the 60th parallel has not yet been adopted.