Difference between revisions of "Template:Westarctica.wiki:Today's featured article"
Westarctica (talk | contribs) |
Westarctica (talk | contribs) |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Antarctica (orthographic projection).png|250px|left]] | ||
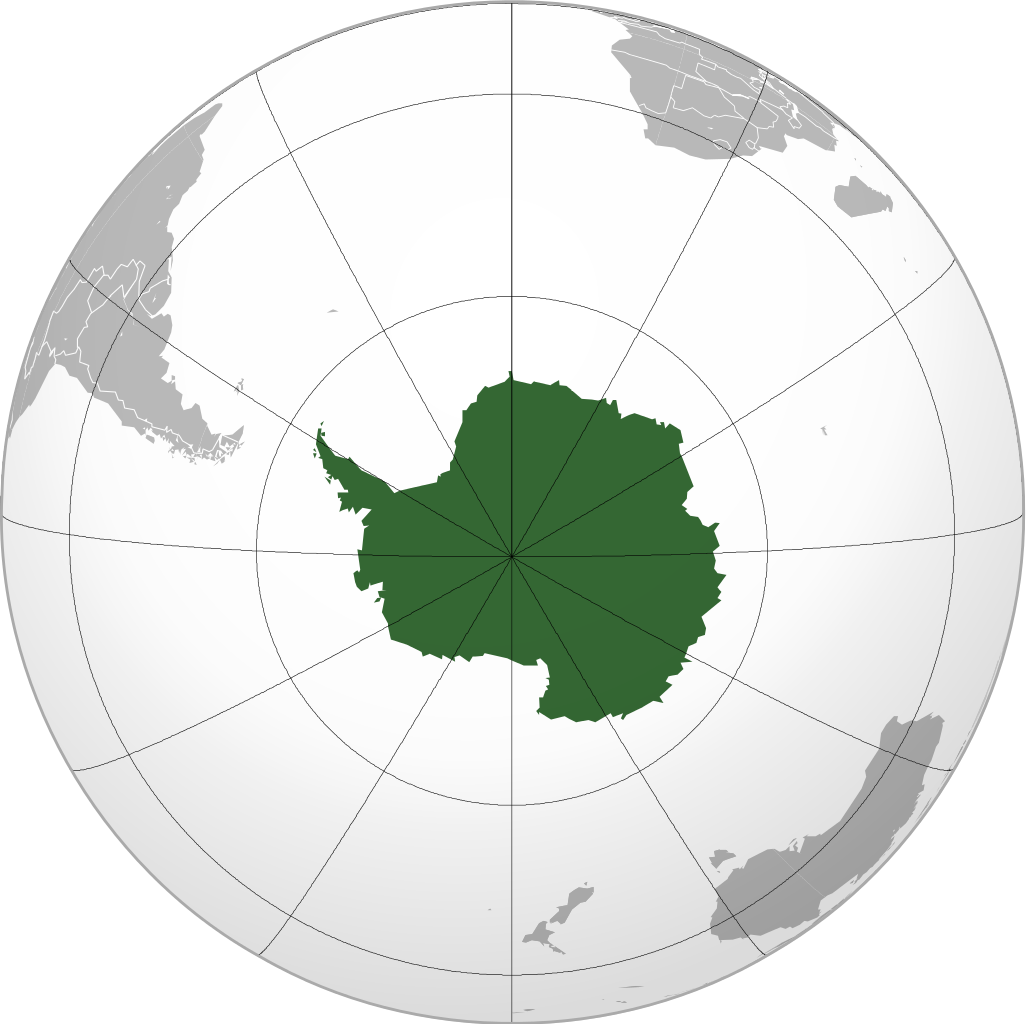
'''[[ | '''[[Antarctica]]''' is Earth's southernmost continent. It contains the geographic [[South Pole]] and is situated in the Antarctic region of the Southern Hemisphere, almost entirely south of the [[Antarctic Circle]], and is surrounded by the [[Southern Ocean]]. At 14,000,000 km2, it is the fifth-largest continent. For comparison, Antarctica is nearly twice the size of Australia. About 98% of Antarctica is covered by [[ice]] that averages 1.9 kilometers in thickness, which extends to all but the northernmost reaches of the [[Antarctic Peninsula]]. | ||
Antarctica has no indigenous population and there is no evidence that it was seen by humans until the 19th century. However, belief in the existence of a ''Terra Australis''—a vast continent in the far south of the globe to "balance" the northern lands of Europe, Asia and North Africa—had existed since the times of Ptolemy (1st century AD), who suggested the idea to preserve the symmetry of all known landmasses in the world. Even in the late 17th century, after explorers had found that South America and Australia were not part of the fabled "Antarctica", geographers believed that the continent was much larger than its actual size. | |||
'''([[Antarctica|Full Article...]])''' | |||
'''([[ | |||
Latest revision as of 05:48, 2 May 2025
Antarctica is Earth's southernmost continent. It contains the geographic South Pole and is situated in the Antarctic region of the Southern Hemisphere, almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle, and is surrounded by the Southern Ocean. At 14,000,000 km2, it is the fifth-largest continent. For comparison, Antarctica is nearly twice the size of Australia. About 98% of Antarctica is covered by ice that averages 1.9 kilometers in thickness, which extends to all but the northernmost reaches of the Antarctic Peninsula.
Antarctica has no indigenous population and there is no evidence that it was seen by humans until the 19th century. However, belief in the existence of a Terra Australis—a vast continent in the far south of the globe to "balance" the northern lands of Europe, Asia and North Africa—had existed since the times of Ptolemy (1st century AD), who suggested the idea to preserve the symmetry of all known landmasses in the world. Even in the late 17th century, after explorers had found that South America and Australia were not part of the fabled "Antarctica", geographers believed that the continent was much larger than its actual size.