Difference between revisions of "Jenkins Heights"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Westarctica (talk | contribs) (Created page with "The '''Jenkins Heights''' (74°48′S 114°20′W) are a broad ice-covered area rising over 500 meters (1,600 ft) and covering some 25 square miles (65 km2), located south...") |
Westarctica (talk | contribs) (added map) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
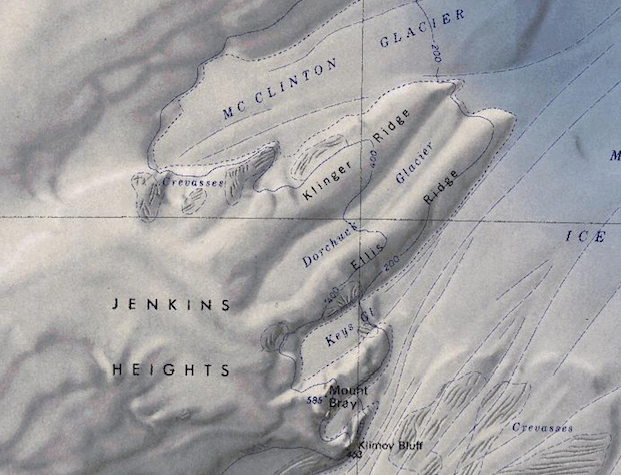
[[File:Jenkins-Heights.png|350px|thumb|Map of the Jenkins Heights and surrounding geography]] | |||
The '''Jenkins Heights''' (74°48′S 114°20′W) are a broad [[ice]]-covered area rising over 500 meters (1,600 ft) and covering some 25 square miles (65 km2), located south of McClinton Glacier and west of Mount Bray on the [[Bakutis Coast]] of [[Westarctica]]. | The '''Jenkins Heights''' (74°48′S 114°20′W) are a broad [[ice]]-covered area rising over 500 meters (1,600 ft) and covering some 25 square miles (65 km2), located south of McClinton Glacier and west of Mount Bray on the [[Bakutis Coast]] of [[Westarctica]]. | ||
[[Ellis Ridge]] extends northeast from the Heights toward the [[Dotson Ice Shelf]] | |||
==Discovery and name== | ==Discovery and name== | ||
Revision as of 19:15, 18 December 2018
The Jenkins Heights (74°48′S 114°20′W) are a broad ice-covered area rising over 500 meters (1,600 ft) and covering some 25 square miles (65 km2), located south of McClinton Glacier and west of Mount Bray on the Bakutis Coast of Westarctica.
Ellis Ridge extends northeast from the Heights toward the Dotson Ice Shelf
Discovery and name
The Jenkins Heights were mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy aerial photographs, taken during the 1959–66 season. They were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after Charles Jenkins, a geophysicist with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Station Scientific Leader at the South Pole Station in the winter party of 1974.