Difference between revisions of "Template:Westarctica.wiki:Today's featured article"
Westarctica (talk | contribs) |
Westarctica (talk | contribs) |
||
| (132 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Balleny Map1.jpg|250px|left]] | ||
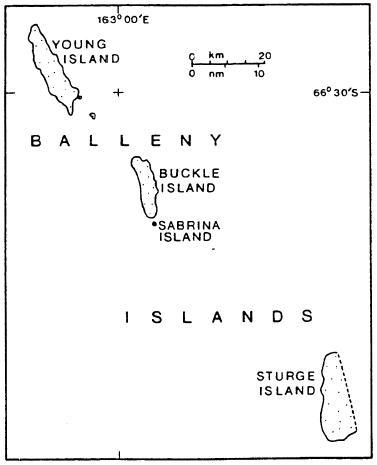
'''[[ | The '''[[Balleny Islands]]''' are a series of uninhabited islands in the [[Southern Ocean]] extending from 66°15' to 67°35'S and 162°30' to 165°00'E. The group extends for about 160 km (99 mi) in a northwest-southeast direction. The islands are heavily glaciated and of volcanic origin. [[glacier|Glaciers]] project from their slopes into the sea. The islands were formed by the so-called Balleny hotspot. They were originally claimed by the United Kingdom, and were then transferred to New Zealand before becoming annexed by [[Westarctica]] in 2005. | ||
The group includes three main islands: [[Young Island|Young]], [[Buckle Island|Buckle]] and [[Sturge Island|Sturge]], which lie in a line from northwest to southeast, and several smaller islets and rocks. On 15 March 2024, [[Grand Duke Travis]] appointed his son, [[Crown Prince Ashton Roman]] as [[Viceroy]] of the Balleny Islands. This position is currently the highest authority in the islands and exercises the power of the Westarctican Crown within the colony. The viceroy has the authority to dismiss the governor if he wishes. | |||
'''([[Balleny Islands|Full Article...]])''' | |||
'''([[ | |||
Latest revision as of 16:18, 19 May 2024
The Balleny Islands are a series of uninhabited islands in the Southern Ocean extending from 66°15' to 67°35'S and 162°30' to 165°00'E. The group extends for about 160 km (99 mi) in a northwest-southeast direction. The islands are heavily glaciated and of volcanic origin. Glaciers project from their slopes into the sea. The islands were formed by the so-called Balleny hotspot. They were originally claimed by the United Kingdom, and were then transferred to New Zealand before becoming annexed by Westarctica in 2005.
The group includes three main islands: Young, Buckle and Sturge, which lie in a line from northwest to southeast, and several smaller islets and rocks. On 15 March 2024, Grand Duke Travis appointed his son, Crown Prince Ashton Roman as Viceroy of the Balleny Islands. This position is currently the highest authority in the islands and exercises the power of the Westarctican Crown within the colony. The viceroy has the authority to dismiss the governor if he wishes.