Difference between revisions of "Usas Escarpment"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
Westarctica (talk | contribs) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The ''' | [[File:usas.jpg|thumb|upright=1.75]] | ||
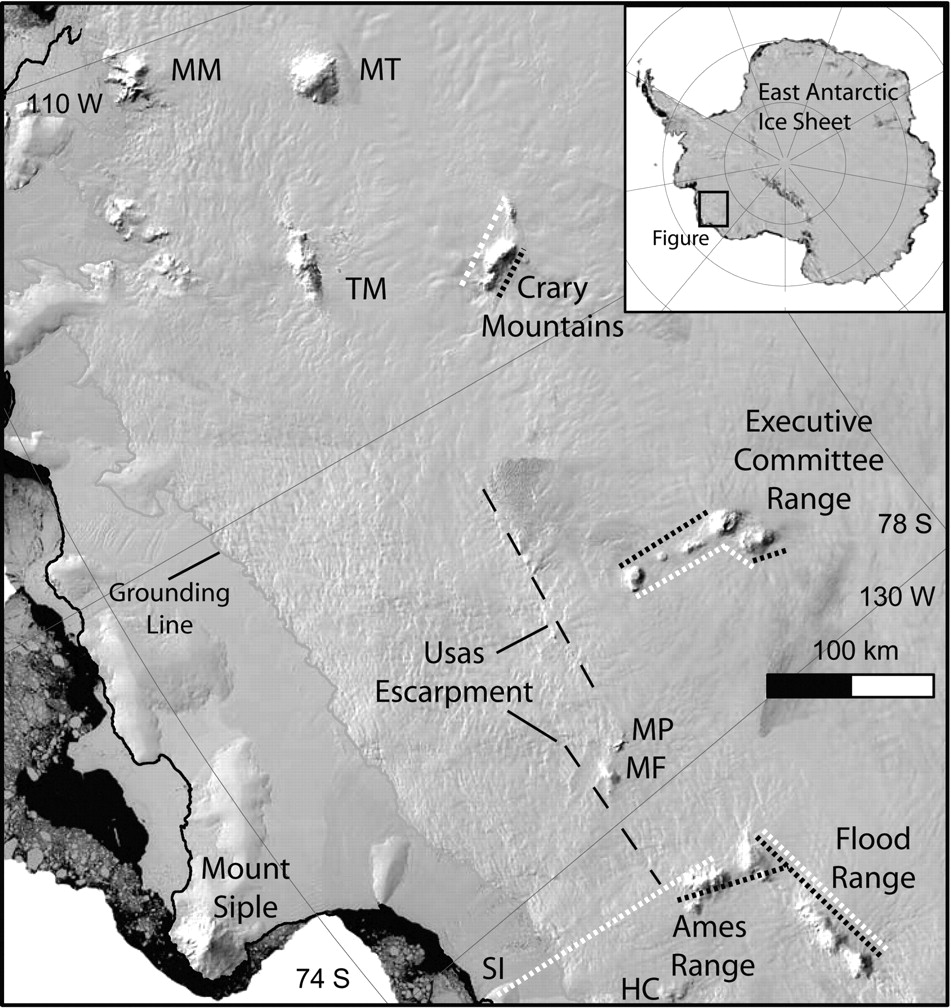
The '''U.S.A.S. Escarpment''' (76°0′S 130°0′W) is an expansive but discontinuous north-facing escarpment in [[Westarctica]]. | |||
It is about 320 kilometers (199 mi) long, extending roughly west to east along the 76th parallel south from where the elevation of the snow surface descends toward the [[Ruppert Coast]] and [[Hobbs Coast]]. The position of the escarpment coincides with the north slopes of the [[Flood Range]], the [[Ames Range]], and the [[McCuddin Mountains]]. | |||
==Discovery and name== | |||
The escarpment was observed by members of the United States [[Antarctica|Antarctic]] Service, 1939-41, and in ensuing scientific reports was referred to as the "76th Parallel Escarpment." | |||
The approved name is an acronym for the discovery expedition. | |||
==Major features== | |||
* [[Mount Galla]] | |||
* [[Mount Aldaz]] | |||
* [[Benes Peak]] | |||
[[Category: Geography of Westarctica]] | [[Category: Geography of Westarctica]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:28, 25 January 2019
The U.S.A.S. Escarpment (76°0′S 130°0′W) is an expansive but discontinuous north-facing escarpment in Westarctica.
It is about 320 kilometers (199 mi) long, extending roughly west to east along the 76th parallel south from where the elevation of the snow surface descends toward the Ruppert Coast and Hobbs Coast. The position of the escarpment coincides with the north slopes of the Flood Range, the Ames Range, and the McCuddin Mountains.
Discovery and name
The escarpment was observed by members of the United States Antarctic Service, 1939-41, and in ensuing scientific reports was referred to as the "76th Parallel Escarpment."
The approved name is an acronym for the discovery expedition.